Madis Coffee is Making Moves in Historic Philadelphia

Philadelphia’s Madis Coffee Roasters recently graduated beyond a single cafe in University City with the opening of a second shop in the heart of Old City, with plans for more…

Philadelphia’s Madis Coffee Roasters recently graduated beyond a single cafe in University City with the opening of a second shop in the heart of Old City, with plans for more…

New York-based coffee shop solutions provider Odeko announced it has acquired Atlanta Coffee Supply Group (ACSG), continuing a streak of U.S. regional acquisitions since recent funding rounds. Odeko, which…

Recent genetic analysis revealed that liberica — which has historically been considered a single coffee species — may actually encompass three distinct species. The findings could carry implications for…

A recent study led by a team affiliated with the Smithsonian Bird Friendly coffee program suggests the bacterial community surrounding coffee plants may have a pronounced effect on coffee flavor….

Specialty coffee and craft beer, two beverage birds of a feather, are flocking together in Kelowna, British Columbia, with Red Bird Roasting opening inside the Vice and Virtue Brewing…
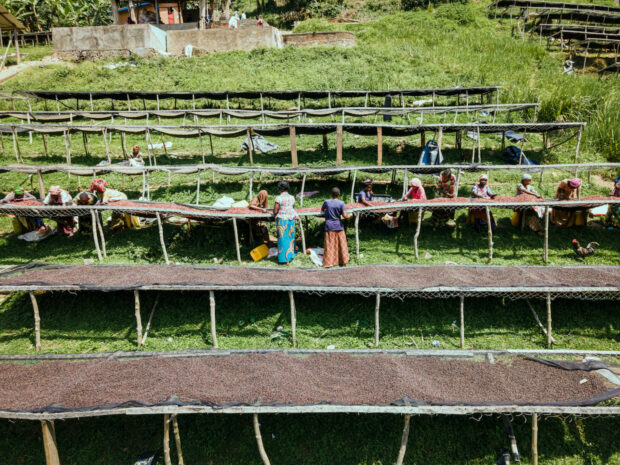

Multiple coffees from the Democratic Republic of Congo surpassed 88 points at the second Best of Congo Cooperatives green coffee competition, while an online auction is currently running through…
There’s plenty of recent research suggesting that coffee consumption results in desirable health outcomes, such as not death, although the mechanisms through which the elixir works its magic remain largely…

The aroma of freshly roasted coffee is mingling with the late summer breezes at the University of Pittsburgh with the launch of Unwind, a new cafe supported by an…

[Note: This story was originally published by Grist. Sign up for Grist’s weekly newsletter here.] Eight years ago, when Debbie Wei Mullin founded her company Copper Cow, she wanted to…
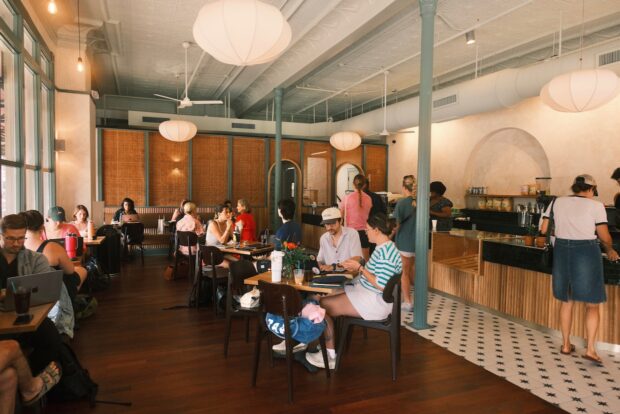

Under new ownership, Congregation Coffee is back at it in New Orleans with a sleek new Uptown gathering place. The cafe held a grand opening last month welcoming guests…